
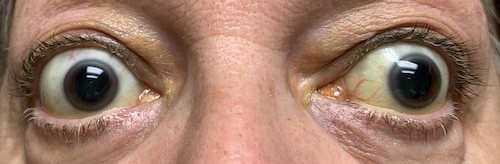
medications that decrease the immune response, such as cyclosporin.Non-surgical options for treatment can include: Surgery can be helpful for those individuals with more severe eye involvement. There are a variety of medical options for exophthalmos. While treating the thyroid problem is important, that alone may not resolve the exophthalmos. If the person has thyroid problems, the doctor will treat the underlying cause and bring thyroid hormone levels back to normal. Smoking has been shown to worsen exophthalmos and make it more difficult to treat. Quitting smoking is recommended for anyone with this condition. Treatment depends on several factors, including the cause, the person’s age, and their general health. The ophthalmologist or eye specialist will monitor the person regularly. Share on Pinterest Eye drops may help relieve dry eyes in cases of exophthalmos. While Graves’ disease is the most common disorder that can cause the eyes to protrude it is not the only one. Other signs and symptoms of Graves’ disease not related to the eyes include irregular heartbeats, anxiety, elevated blood pressure, increased appetite, weight loss, diarrhea, and sleeping problems. feeling pressure behind and around the eyes.difficulty in moving eyes, as the eye muscles are affected.blindness if the optic nerve is compressed.diplopia, or double vision caused by weakening of the eye muscles.lacrimation, or eye secretions, and shedding of tears.SymptomsĪ person who has Graves’ exophthalmos may experience the following symptoms: The fatty tissue and muscles around the eye become large, pushing the eye forward and out. The immune cells that attack the thyroid in Graves’ disease also accumulate within the eye socket. Interestingly, eye involvement can occur up to 10 years before the diagnosis of thyroid problems is made and up to 20 years after. Anywhere from 25-50 percent of people with this condition will have an eye involvement. Graves’ disease is the most common cause of exophthalmos. Share on Pinterest Exophthalmos is a symptom of Graves’ disease. The autoimmune antibodies can attack the muscles and soft tissue surrounding the eyes, which can cause them to protrude from the sockets. If a person’s immune system attacks the thyroid gland, it may react by producing extra hormones. Experts are not sure why autoimmune diseases occur. Graves’ disease is an example of such an autoimmune reaction. This is described as an autoimmune reaction. However, in certain people, the immune system starts attacking normal tissue. These include some bacteria, viruses, parasites, cancer cells, and fungi. In a healthy person, the immune system attacks pathogens, the organisms and substances that are bad for us. It may take some time for this to happen. Hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism may not cause the eyes to protrude immediately. It is often due to hyperthyroidism, and sometimes to hypothyroidism, which is caused by an underactive thyroid gland. Thyroid eye disease is a condition where the soft tissues and muscles around the eyes become swollen and inflamed. The hormones are called thyroxine and triiodothyronine, and they are normally kept in balance. The hormones it produces help to regulate growth, the rate of metabolism and other important functions of the body. The thyroid is in the neck, below the Adam’s apple. A person with hyperthyroidism has an overactive thyroid gland that produces excess hormones and causes it to grow. Graves’ disease is an autoimmune disease that causes hyperthyroidism.


Share on Pinterest Graves’ disease affects the thyroid gland.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
